Introduction, what is a stablecoin?
Stablecoin are digital currencies or tokens that are tied to the value of real things. It’s often an asset with a fixed price and purchasing power.
The US dollar is a common example of a stablecoin, or asset that may be tied to a stable state. Alternatively, it might resemble a commodity like silver or gold. It is generally something we can predict with some degree of certainty.
To put it another way, the price of a stablecoin is fixed in relation to another dependable asset, such as the US dollar. Thus, 1 USD equals 1 unit of stable cryptocurrency coin.
Stablecoin Price:
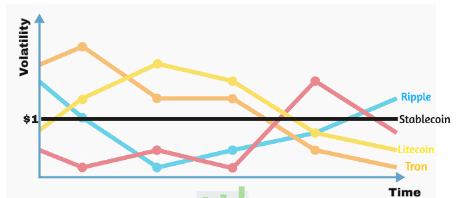
The principle is rather basic. The price of a stablecoin stays constant, as the name indicates.
Quite apparent, really!
Stable coins have a considerably more stable value than traditional bitcoin currencies. This is useful if you want to transmit and store value using cryptocurrencies.
Now that we’ve defined stablecoins, we need to understand the many types that exist. Stablecoins exist in a wide range.
The Stablecoin List:
The three major topics we shall address are the following:
- Cash-backed stablecoins, also known as pegged stablecoins.
- Stablecoin collateral
- Stablecoin centralized
Now, let’s examine more closely into peg stablecoins and how they operate.
A Peg Stablecoin: What Is It?
Fiat-backed stablecoins, also known as peg stablecoins, are rather easy to understand. A peg stablecoin is created when a certain kind of token or cryptocurrency is used to disguise a pegged asset that supports it. As a result, we know that if you hold a single US dollar cryptocurrency coin, it is somehow supported by the dollar.
Tether helped stablecoins gain popularity. They were the first pegged stablecoin, established in 2014.
Tether Limited is the company responsible for the tether tokens’ release. This firm backs a specific number of Tether currencies listed on cryptocurrency exchanges, with millions of dollars in reserves stored in banks throughout the world.
Top examples of fiat-backed stablecoins:
- Tether
- RealUSD
- Gemini Dollars
- USD coin
What is a Collateralized Stablecoin (CS)?
The operation of collateralized stablecoins is identical to that of fiat-backed stablecoins. The main difference is that they are not backed by fiat money, but rather by the reserves of another cryptocurrency.
Collateralized stablecoins are ones that rely on a set of assets or collateral to keep them fresh. The capacity of the whole ecosystem to exist on the blockchain is the key advantage of crypto-collateralized stablecoins.
The two most well-known examples of crypto-collateralized stablecoins are Maker and DAI stablecoin.
The DAI stablecoin predominantly uses Ethereum tokens as collateral.
They do, however, want to back the DAI stablecoin with a wide range of assets over time.
The second advantage of collateralized stablecoins is that they are completely decentralized. This indicates that they can take use of the blockchain’s inherent advantages. They may also be disposed of swiftly and economically. The public storing of all transactions makes the ecosystem as a whole transparent.
Volatility is the primary issue with collateralized stablecoins. They are far less stable than currencies backed by money.
The algorithmic stablecoins do not need a peg or collateral. How do they assure that one coin is worth one US dollar?
Algorithmic stablecoins do this by adjusting supply in response to demand. Basic economics has taught us that supply and demand always reach an equilibrium point. You can alter the supply to influence the price of anything. Supply fluctuations cause the equilibrium point to move, affecting price in the long run.
These stablecoins are completely decentralized, independent of banks, and collateral-free. Furthermore, there is a complete split with the fiat monetary system.
Reserve, Basis, and Carbon are excellent instances of algorithmic stablecoins.
Now that we’ve established that there are significant distinctions between these stablecoins, we’ll go over some of their use cases. So, how do stablecoins function?
How do stablecoins work?
The functioning of stablecoins depending on their category has already been briefly discussed. To provide a more detailed explanation, we’d want to take a step further and employ DAI stablecoin.
A DI Stablecoins are cryptocurrency inventions made possible by borrowing from the Maker platform. Furthermore, DAI is associated with the US dollar, the world’s primary reserve currency.
Tired of losing trades? Open a Libertex account to start trading stocks and forex with the professionals today.
Assume you are an entrepreneur in need of financing to grow your business.
Lending money into a collateralized debt position enables you to borrow DAI stablecoins. You may always recover your collateral by returning the DAI stablecoins you borrowed. You will also be required to pay an additional transfer fee.
How are DAI coins created?
A burned Maker cryptocurrency must be acquired every time a DAI coin is minted. Additionally, you must give some security. Ethereum is now used as collateral.
Essentially, you burn Maker to generate DAI stablecoin. Maker will suffer more burns if you think the DAI will grow more famous in the future. Given this, Maker’s price is likely to rise in the long run.
Here’s how the DAI stablecoin generation method works:
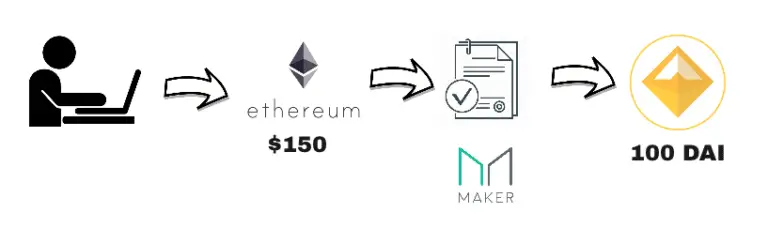
To produce 100 DAI, you must submit a smart contract with $150 worth of ETH. Smart contracts are referred to as collateralized debt positions.
To get $150 in ETH, you must return your 100 DAI stablecoins. You will have to pay a little fee in Maker for this. As we previously stated, this method causes some Maker to be burnt.
Let us now look into how DAI stablecoin maintains its $1 price.
Assume DAI falls to $0.80 and trades under $1. As a consequence, obtaining the 100 DAI will be less costly, and in order to recover your 150 ETH, you will need to buy more DAI at a lower price. If DAI is less costly, demand will increase, ultimately raising the price of DAI until the arbitrage is no longer sustainable.
If the price of DAI stablecoin exceeds $1, the same mechanism is followed in reverse.
This $1 soft peg will be used as the core of a self-stabilizing gadget.
Stablecoins have a broad variety of uses, but their many advantages will largely illustrate why we even need them:
- They make it easy and inexpensive for consumers to pay out.
- Their low volatility makes them valuable in real-world applications.
- Increase global access to stable money. This is really important!
- Stablecoins may be used as collateral. Lending amongst peers is an excellent example.
To summarize, what precisely is a stablecoin.
Stablecoins have the potential to accelerate the general adoption of cryptocurrency. Stablecoins are beneficial if you understand how they work and how they may help firms pay staff using Bitcoin.
Stablecoins were a big deal in 2019, and many cryptocurrency aficionados are eager to see what this cutting-edge coin has in store for the future. However, the cryptocurrency community understands that the hype around cryptocurrencies seldom materializes. In the future, stablecoins will need a high level of strategic thinking. You can also read;6 Best Cryptocurrency Investment Strategy for 2024
The global adoption of cryptocurrencies will very certainly include the DAI stablecoin.
Follow for the latest news and information Telegram Channel




